
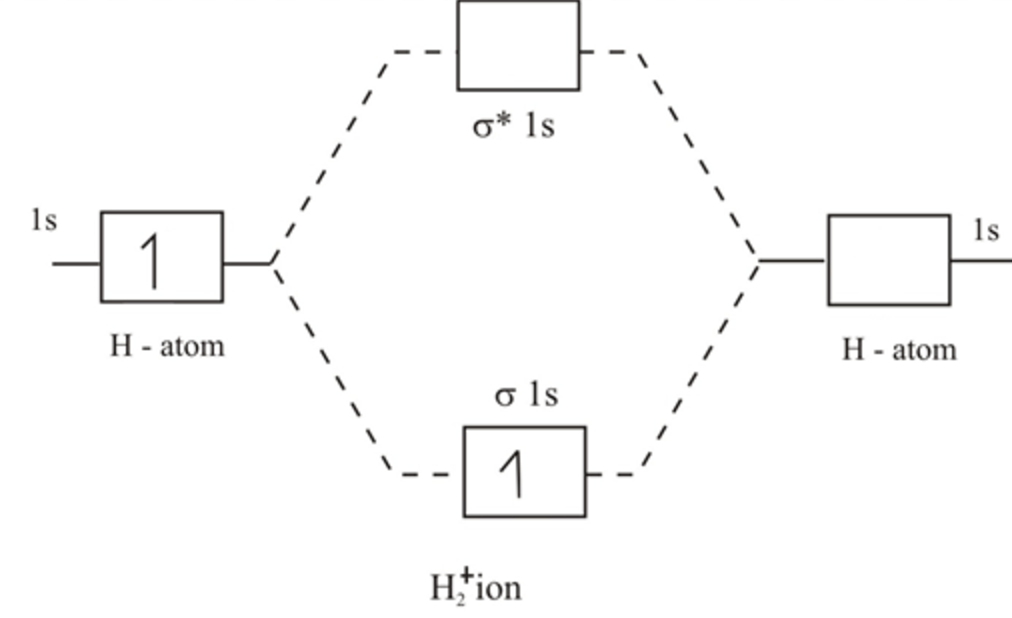
Again, in the MO, there is no unpaired electron, so H 2 is diamagnetic.
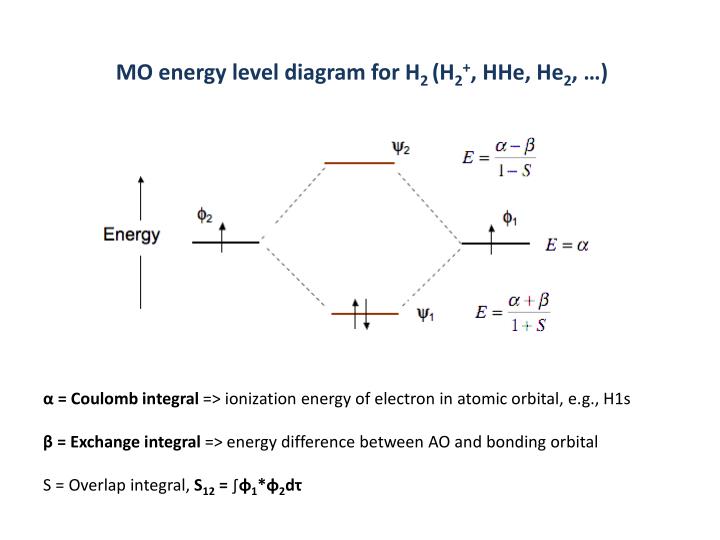
At very long distances, there is essentially no difference in energy between the in-phase and out-of-phase combinations of H 1s orbitals. The H2 molecular orbital diagram is much simpler, because a hydrogen atom only contains 1 electron. For H 2, bond order 1/2 (2-0) 1, which means H 2 has only one bond. Take care while calculating the bond order. The bond order can be determined by substituting those values using bond order formula. The energies of bonding and antibonding orbitals depend strongly on the distance between atoms. Molecular orbital diagram of hydrogen molecule: Bond order: From the molecular orbital diagram, there are 2 electrons in bonding molecular orbital and there is no anti bonding molecular orbital. Greater value of bond order for H2 molecule than H2+ ion shows that two H. The middle of the diagram is just the molecular orbital energy diagram. Bond order value of 1 means that two hydrogen atoms are connected by a single bond. They will be unequal when there is an energy difference between the AOs, for example when a hydrogen 1s orbital and a chlorine 3p orbital combine to make a polar H-Cl bond. What we see here is a molecular orbital interaction diagram. The coefficients c 1 and c 2 will be equal (or nearly so) when the two AOs from which they are constructed are the same, e.g., when two hydrogen 1s orbitals combine to make bonding and antibonding MOs in H 2.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
